Posts Categorized: General
Correctly claiming your home office expenses

With the start of a new financial year it is timely to explore how to correctly claiming your home office expenses.
Can I claim home office expenses?
Yes you can if:-
- You are undertaking genuine employment related activities, or
- Home is your sole base of operations (which includes employees who are not provided with an office, or
- You are carrying on a business from home.
What can home office expenses can I claim?
You can claiming running costs such as:-
- Heat, light and power
- Phone expenses
- Internet
- Consumables such as computer supplies and printing & stationery items
Those who run a business from home or it is their sole base of operations can also claim occupancy costs.
How can I quantify my claim?
There are two available methods:-
- Fixed rate method
- Actual expenses
How does the fixed rate method work?
Under this method, one claims 67 cents for every hour worked at home. Occasionally checking emails doesn’t is not sufficient to allow a claim.
To qualify to sue this method you must incur at least one of the following expenses:-
- Electricity or gas for heating and/or cooling or to power equipment.
- Internet
- Mobile or home phone
- Printing and stationery.
Receipts must be kept to evidence one or more of these costs have been incurred.
And additional to this claim is the depreciation of any home office work items.
TRAP Irrespective of how much you may genuinely use your mobile away from your home office, you will not be able to make a separate claim for using that mobile.
TIP You don’t need to have a set aside office only used for work purposes. You just need a dedicated area.
TIP Once can also claim for hours worked at a holiday home (provided above criteria satisfied).
What records do I need to keep under the cents per hour method?
In addition to the receipts above, as we have highlighted in past posts and Tax Return covering letters, you have been required since February 2023 to log every hour worked at home.
TIP As stated above, you can only claim hours you have logged. You can download a spreadsheet below that is set to track very hour worked at home.
TIP We recommend downloading the spreadsheet below and saving it in the middle of your desktop or laptop – that way you won’t forget to log the hours as you work them.
You can download the home office cents per hour method by clicking here – 2024-25-Home-Office-Expenses-hours-worked-log
What is included within an occupancy home office expenses claim?
One first measures and calculates the area that is used for work/business purposes.
The work/business area % is then applied to:-
- Heat, light and power costs.
- Rent paid
- Mortgage interest
- Council & water rates
- Insurance
However, the area that is claimed under this method means that the Capital Gains tax Principal Residence is lost on the claimed area for the years claimed.
Please call us if you wish to discuss your claim in greater details.
Can you benefit from catch-up super contributions?

It’s that time of year when people are looking for tax deductions. The relatively new catch-up concessional contribution system may be ideal for some.
Long gone are the days when contributions of more than $100,000 could be made into super.
And now that the deducible contribution limit is just $27,500 it just doesn’t leave much to fund for retirement after taking out 15% contribution tax and life insurance premiums. And this low limit becomes more of problem if one doesn’t use their limit in any year(s).
This low limit particularly hurts those who leave the workforce to bring up children. The same can also be said for those who have a couple of tough years financially. This is particularly true of many Victorian business owners during covid and beyond.
The catch up concessional system allows some to contribute more than the $27,500 limit for which a tax deduction can be claimed for the full amount.
To qualify to make a catch-up concessional contribution before 30th June 2024 one must:-
- Have less than $500,000 in super as at 30th June 2023.
- Not used all of one’s limit in any year from 2018/19 to 2022/23.
- Must qualify to be able to make a contribution.
This year is particularly important as it is the first year an unused year will drop off. That is, if you didn’t have concessional contributions of $25,000 accepted by your super fund(s) in the 2018/19 year, that shortfall will be lost if not used by the end of this month.
Things to be wary or mindful of:-
- Some super funds cease accepting contributions by Monday 24th
- The 30th June falls on a Sunday. Those with their own self managed super fund need to avoid making a contribution (banking transfer) after cut off time on Friday 28th June as it will be treated as a contribution in July. That is next financial year.
- And that problem becomes doubly worse if you are not able to make a contribution in July 2024.
- A contribution may not suit you from a tax perspective this year as your income may be too low.
- Or perhaps it is a good year to trigger a capital gain.
- Those with incomes over $250,000 need to be mindful of the extra 15% tax on contributions (and be mindful of how Section 293 income is defined).
- A catch-up concessional contribution cannot be accessed one satisfies what is called a “condition of release” is satisfied (with the main one becoming retired).
So there are many factors to take into consideration.
Whether you should or shouldn’t make a catch up concessional contribution is best done by receiving personal financial planning advice. Such personal advice will address your current situation and future goals and needs. Please let us know if you would like a referral.
2024 super co-contribution

Under the super co-contribution scheme, the government will contribute $1 for every $2 of personal contributions made by an employed or self employed person.
The maximum government co-contribution is $500. So if you wish to target the full $500, you will need to contribute $1,000.
To be qualify, one must:-
- Be employed with their employer paying the compulsory SGC or be a self employed person running a business.
- Have 10% or more of one’s income coming from employment and/or a sole trader business.
- Be less than 71 at the end of the financial year.
- Have combined assessable income (that being income before deductions), Reportable Fringe Benefits (RFBA) and employer super contributions in excess of basic SGC amount (RESC) of less than $60,400.
- Have paid a non-deductible contribution into superannuation from after tax money by 30thJune 2024. This means the contribution must be made from a personal or joint bank account.
- Not be a temporary visa holder.
- Lodge a Tax Return for the year ending 30thJune 2024.
- The maximum co-contribution for a personal contribution of $1,000 is $500 if your combined assessable income is under $45,400. Thereafter it progressively reduces by 3.333 cents for every dollar in excess of $45,400. There is no entitlement if your combined assessable income exceeds $60,400.
- Not have contributed more than your non-concessional cap.
- Have a total super balance under the Transfer Balance Cap (between $1,800,000 and $1,900,000).
If you want to find out what you might be entitled to, click on the following link to the ATO’s calculator here
Other matters to note are:-
- One’s own contribution and that made by the government will be preserved. That is, one will not be able to access it until one retires or satisfies another condition of release.
- The ATO will deposit the co-contribution into one’s super account once they have reconciled one’s lodged 2024 Tax Return with the information provided by one’s super fund(s). Consequently, most co-contributions will not be credited until at least January 2025.
- If your super is with a public or employer superannuation fund, you will need to ensure they accept such contributions. You also need to obtain the appropriate form.
- You will need to make your contribution well before 28th June (as 30th June falls on a Sunday). For those with your own SMSF, your fund can only accept such a contribution if permitted by its trust deed. We will take no responsibility where a client does not consult with us beforehand.
What is best for you depends on your circumstances and take into account a large number of considerations.
You should therefore seek financial planning advice to ensure such a contribution will work as intended and is in your best overall interests.
Tips and traps in the 2024 Federal Budget
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stage 3 tax cuts and you

After much speculation, the Government has announced that they will amend the legislated Stage 3 tax cuts scheduled to commence on 1 July 2024. This will mean that more Australian taxpayers will receive a personal income tax cut and take home more in their pay packet from 1 July, but for some, the impact will be less favourable than it would have been prior to the redesign.
What will change?
The revised tax cuts redistribute the reforms to benefit lower income households that have been disproportionately impacted by cost of living pressures.
So under the proposed redesign, all resident taxpayers with taxable income under $146,486, who would actually have an income tax liability, will receive a larger tax cut compared with the existing Stage 3 plan. For example:
- An individual with taxable income of $40,000 will receive a tax cut of $654, in contrast to receiving no tax cut under the current Stage 3 plan (but they are likely to have benefited from the tax cuts at Stage 1 and Stage 2).
- And an individual with taxable income of $100,000 would receive a tax cut of $2,179, which is $804 more than under the current Stage 3 plan.
However, an individual earning $200,000 will have the benefit of the Stage 3 plan slashed to around half of what was expected from $9,075 to $4,529. There is still a benefit compared with current tax rates, just not as much.
There is additional relief for low-income earners with the Medicare Levy low-income thresholds expected to increase by 7.1% in line with inflation. It is expected that an individual will not start paying the 2% Medicare Levy until their income reaches $32,500 (up from $26,000).
While the proposed redesign is intended to be broadly revenue neutral compared with the existing budgeted Stage 3 plan, it will cost around $1bn more over the next four years before bracket creep starts to diminish the gains.
How did we get here?
Tax cuts delivered in 3 stages were first announced in the 2018-19 Federal Budget. The personal income tax plan was designed to address the very real issue of ‘bracket creep’ – tax rates not keeping pace with growth in wages and increasing the tax paid by individuals over time.
The three stage plan sought to restructure the personal income tax rates by simplifying the tax thresholds and rates, reducing the tax burden on many individuals and bringing Australia into line with some of our neighbours (i.e., New Zealand’s top marginal tax rate is 39% applying to incomes above $180,000).
Stage 1 tax cuts took effect from 1st July 2018.
Stage 2 tax cuts took effect from 1st July 2020.
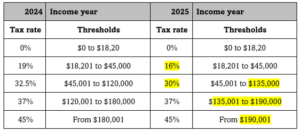
Stage 3 as legislated were due to to take effect from 1 July 2024 – but will now change as per the following table.
The current, legislated and re-designed Stage 3 rates for Australian tax residents are:-
| Tax rate | 2023-24 | 2024-25 legislated | 2024-25 proposed |
| 0% | $0 – $18,200 | $0 – $18,200 | $0 – $18,200 |
| 16% | $18,201 – $45,000 | ||
| 19% | $18,201 – $45,000 | $18,201 – $45,000 | |
| 30% | $45,001 – $200,000 | $45,001 – $135,000 | |
| 32.5% | $45,001 – $120,000 | ||
| 37% | $120,001 – $180,000 | $135,001 – $190,000 | |
| 45% | >$180,000 | >$200,000 | >$190,000 |
Any concerns?
If you have any concerns about the impact of the proposed changes please just give us a call.
Christmas & tax (& FBT & GST)

Entertaining and providing gifts at Christmas time to staff, customers and suppliers is a cost of doing business. However, there are some important FBT, GST and income tax considerations and outcomes to keep in mind.
As an employer, you need to be careful at what you provide at Christmas. The rules are complex and the costs of getting it wrong can prove very expensive.
We will outline some of the more common scenarios and what to be careful of.
Under-pinning the implications are the following key points:-
- Christmas parties, entertainment and gifts are all treated under entertainment tax rules.
- FBT applies to benefits given to employees.
- There are no FBT implications on entertainment and gifts given to customers, clients and suppliers.
- A business can adopt one of three methods to quantify the taxable components of any entertainment expenditure – in fact there are 38 permutations depending on who is entertained where, how and with whom. We will largely address the actual method which is the one used by most small businesses (as it usually results in the best outcome). It is beyond the scope of this briefing to address the 12 week log method and we will only touch upon the 50/50 method where relevant.
- Christmas comes but once a year and to the best of my knowledge and experience does so on 25th Nevertheless, the ATO treats Christmas parties and gifts as being what are called minor, infrequent and irregular benefits.
- Such minor benefits are FBT exempt where they cost less than $300 (including GST) provided the actual method is used to quantify entertainment.
The Christmas party
Where entertainment is calculated under the actual expenditure method (which is the most common method for small businesses):-
- A Christmas party is held on-site on a work day, the whole cost for each employee will be an exempt fringe benefit. So too will the spouse’s cost provided the cost per spouse is less than $300. No income tax deduction can be claimed for the cost of the party including that in respect of any family members that may attend. Taxi travel to or from the workplace (not both ways) will be exempt from FBT and not tax deductible.
- When a Christmas party is held off the work premises, then the whole cost will be exempt from FBT provided the party costs less than $300 per person (employees and their spouses). No income tax deduction can be claimed for the cost of the party including that in respect of any family members that may attend.
- If an external Christmas party costs more than $300 or more per person then the total cost is subject to FBT.
- The cost of any entertainment provided during the party (whether that be at the work premises or outside) will be exempt if it costs less than $300 per head – for example a DJ, musician, clown and comedian.
- The cost of entertaining clients, customers and suppliers is not subject to FBT and is not tax deductible.
- Where any exemption is exceeded then FBT is payable. Consequently, an FBT Tax Return must be lodged and FBT paid (the FBT tax rate being the same as the top marginal tax rate). Please keep this in mind when completing the 2018/19 FBT Questionnaire in early April 2019.
- All other entertainment during the year will be subject to FBT on a case by case basis.
Where entertainment is calculated under the 50/50 method:-
- 50% of the cost will be subject to FBT and this portion will be tax deductible. The other 50% will not be subject to FBT and will not be tax deductible. An FBT Tax Return must be lodged and FBT paid.
- Only taxi travel from home to the venue will be FBT exempt and not deductible for tax.
- 50% of all other entertainment during the year will be subject to FBT.
Gifts
The following gifts are exempt from FBT and are tax deductible:-
- Hampers, bottles of wine, gift vouchers, a pen set costing less than $300 (inclusive of GST).
The following gifts are subject to FBT and are not tax deductible:-
- Tickets to a sporting event or theatre, holiday, accommodation, etc.
The GST treatment of gifts is:-
- That the GST component of any tax deductible portion can be claimed back.
- But the GST component that relates to the non tax deductible portion can’t be claimed.
Please do not hesitate to call us should you have any queries.
Small businesses protection against unfair contract laws

Unfair contract laws to protect small businesses were introduced in 2016. We are pleased to report that as of Thursday 9th November, they have substantially tightened.
One of the main changes is that fines can now be imposed against those enforcing unfair contract terms on small businesses. Those fines are up to $2,500,000 for individuals and $50,000,000 for corporations. Previously there were no fines. Now these laws have some teeth!
Furthermore, a person who breaches the new rules can be disqualified from being a director for up to 6 years.
Following are some examples of unfair contract laws (where it gives one party but not the other):-
- Vary the terms of a contract.
- Terminate a contract.
- Renew or not renew a contract.
- Apply penalties to the other party for a breach of contract.
- Vary the price payable without the other party having the right to terminate the contract.
- Vary the characteristics of the contracted goods or services.
- Restrict one party’s right to the sue the other party.
- Another important change is the definition of a small business has been increased from 20 to 100 full and part time employees.
The somewhat recent small business protection now really has some teeth. Moreover, it will act as a deterrent against those who have unfairly acted against small businesses in the past.
Please contact us if you would like a referral for a unfair contract matter to a qualified lawyer.
Two important WorkCover obligations

It’s a busy time of year and therefore timely to remind you of two important WorkCover obligations.
Injured at work posted
One of the fundamental WorkCover obligations is to display the If you are injured at work poster.
If a Victorian WorkCover official visits you then they ask to see it. And you will be fined if you don’t have it displayed.
Please note that this poster is to be displayed at each work location.
If you don’t have a copy you can download a copy at – click here
If you employ workers (and some types of contractors) interstate then you will also need to comply with that state or territory’s obligations.
WorkCover remuneration certification
It may be time to complete your 2023 WorkCover remuneration certification.
Large employers are required to submit early. Other employers have delayed lodgement dates. That said, it still may be in your interest to lodge soon. This is particularly the case if your remuneration will be significantly less in 2023/24 than for 2022/23.
You will get back what you over pay based off their estimate; but why over pay in the first place.
You will also ensure it is lodged. Many employers forget to lodge and suffer from WorkCover’s default 20% annual increase. So get it done now when you have finalised and issued the PAYG Payment Summaries.
Casual employee obligations

Casual employee – probably the most misunderstood employment term!
Whether your employee is causal or not is a question of fact. Yet stories abound about employers wrongly classifying employees as casual. As soon as there is regularity of days and/or hours then they are not casual. In particular, someone who works say Tuesdays, Thursdays and Fridays is not a casual employee; they are permanent part time.
So what is the risk of classifying someone incorrectly as a casual employee?
You might well have paid them a 25% loading – but if they go off to Fair Work Australia and win then you will have to pay leave entitlements on top of that 25%.
It may have been lost during covid, but employers are now required annually to offer casual employees full or part time work. You can read more at – https://www.mrsaccountants.com.au/important-action-if-you-employ-casual-employees/
Employees have the right to request full or part time work.
Employers with more than 15 employees are required to:-
- Offer casual conversion at least annually.
- Make a written offer within 21 days of anniversary.
- If not offering conversion, notify the employee within 21 days (including reason).
These requirements provide a clear framework for employers to adhere to. Don’t expect to win any dispute if you have not followed these rules.
Please contact us if you would like a referral to an employment specialist.
Reminder about new home office deductions rules

We are returning to the important changes to home office deductions; in particular, how the ATO now requires you to prove the hours you have worked from home to continue to claim under the cents per hour / fixed rate method.
You need to comply with the new requirements in order to make a claim for this 2023/24 year. We cannot emphasise enough the requirement to keep actual records of all hours worked at home or have access to timesheets or roster records (if kept/accessible).
What are the key changes?
The ATO has re-set the rules for taxpayers who are working from home and wish to claim deductions based on either:
- actual expenses, or
- revised fix rate method of 67 cents per hour.
A key and indeed welcome change is that you do not need to have a separate home office or dedicated work area set aside in your home in order to rely on the fixed rate method.
Also, if more than one individual is working from home at the same time, each individual will be able to apply the fixed rate method if they each meet the requirements listed above.
To be eligible to claim tax deductions for working from home expenses, you must:
- incur additional running expenses as a result of working from home
- be working from home to fulfil your employment duties, not just completing minimal tasks
- keep records at the time you work to prove you incur the cost.
Revised Fixed Rate Method
The revised fix rate method:
- has increased from 52 cents to 67 cents per hour worked from home
- removes the requirement to have a dedicated home office space
- includes claims for:
- data and internet
- mobile and home phone usage
- electricity and gas
- computer consumables (e.g. printer ink)
- stationery
- allows taxpayers to separately claim the work-related portion of:
- immediate deduction for items that cost less than $300 (e.g. keyboards, computer mouses, power boards, desk lamps and chargers)
- depreciation of office furniture and computers (items that cost more than $300)
- repairs and maintenance of these assets
- cleaning (only if you have a dedicated home office)
Actual Cost Method
The actual cost method allows you to claim a tax deduction for the actual expenses you incur as a result of working from home.
Using this method, you are required to keep an invoice/receipt for every expense you claim.
Expenses You Can’t Claim
The ATO has stated that you can’t claim a tax deduction for:
- coffee, tea, milk and other general household items, even if your employer may provide these at work
- costs that relate to your children’s education, such as equipment you buy – for example, iPads and desks, subscriptions for online learning
- items your employer provides – for example, a laptop or a mobile phone
- expenses where your employer reimburses you for the cost.
VERY IMPORTANT: The records you need to keep for the fixed rate method
You need to keep record of the total number of actual hours you worked from home to prove your fixed rate method working from home tax deductions for the 2024 financial year onwards.
To claim your working from home deduction using this method, you must keep:
- a record of the number of actual hours you work from home during the entire income year – for example, a timesheet, roster, diary or other similar document.
- at least one record for each of the additional running expenses you incur that the rate per work hour includes – for example, if you incurred electricity and stationery expenses keep one quarterly bill for your electricity expenses and one receipt for your stationery expenses.
Next steps
It has come to our attention that some clients have not been keeping record of the hours worked at home – that being one of:-
- timesheets
- rosters
- a diary or similar document kept contemporaneously.
We have therefore built a spreadsheet for you to use and which you can download here – 2023-24 Home Office Expenses – hours worked log
You must also keep evidence for each of the additional running expenses that you incurred. The documents you need to keep in order to demonstrate that you have incurred additional running expenses must show what the expense is and that you incurred the expense.
For energy, mobile and/or home telephone and internet expenses, you must keep one monthly or quarterly bill. If the bill is not in your name, you will also have to keep additional evidence showing you incurred the expenses; for example, a joint credit card statement showing payment or a lease agreement showing you share the property, and therefore the expenses, with others.
For stationery and computer consumables, which are occasional expenses, you must keep one receipt for each item purchased.
Please feel free to contact our office and speak with one of our expert accountants if you need any assistance with this so we can help you to maximise your tax deductions in your 2024 and future year Tax Returns.